Laser-Tag Robot

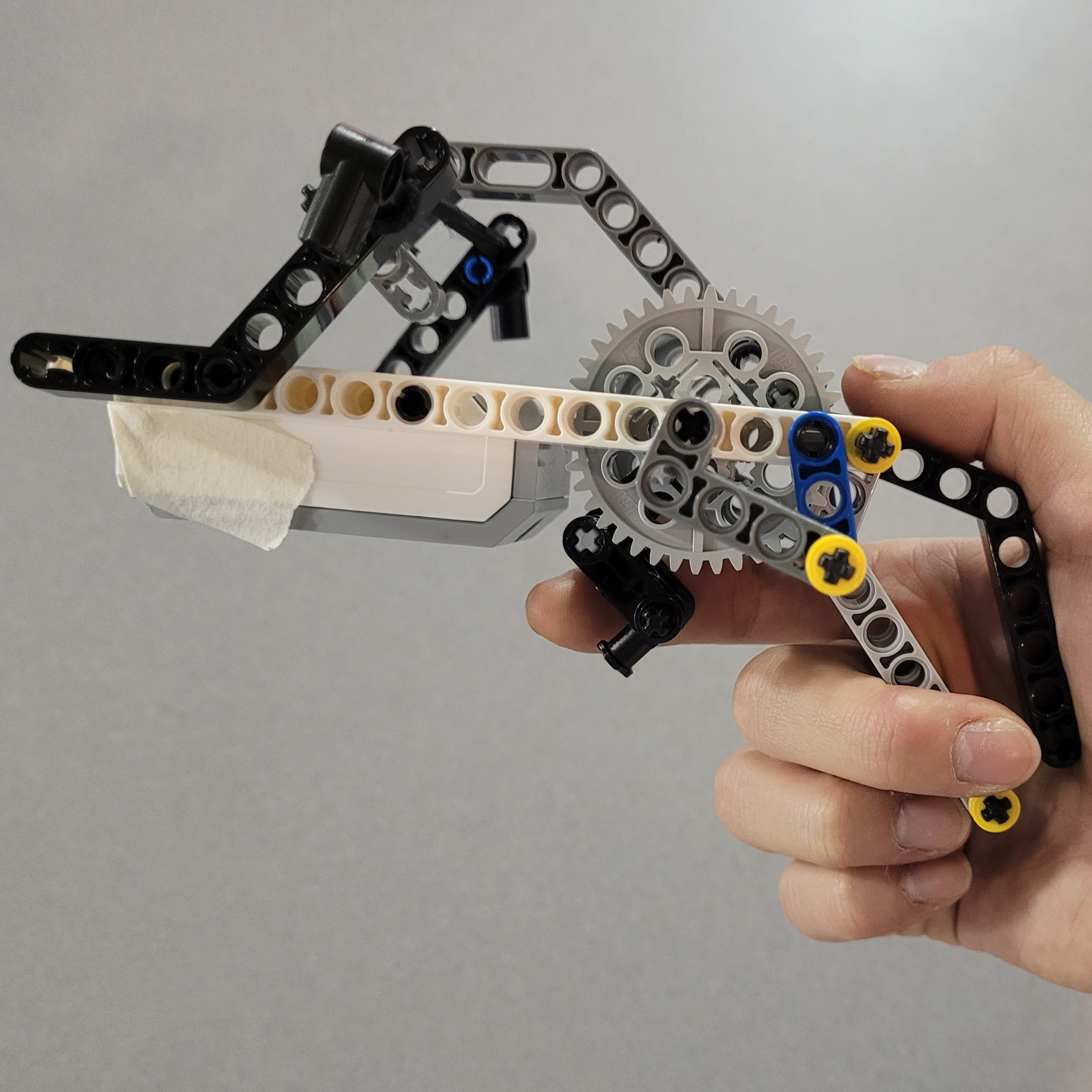
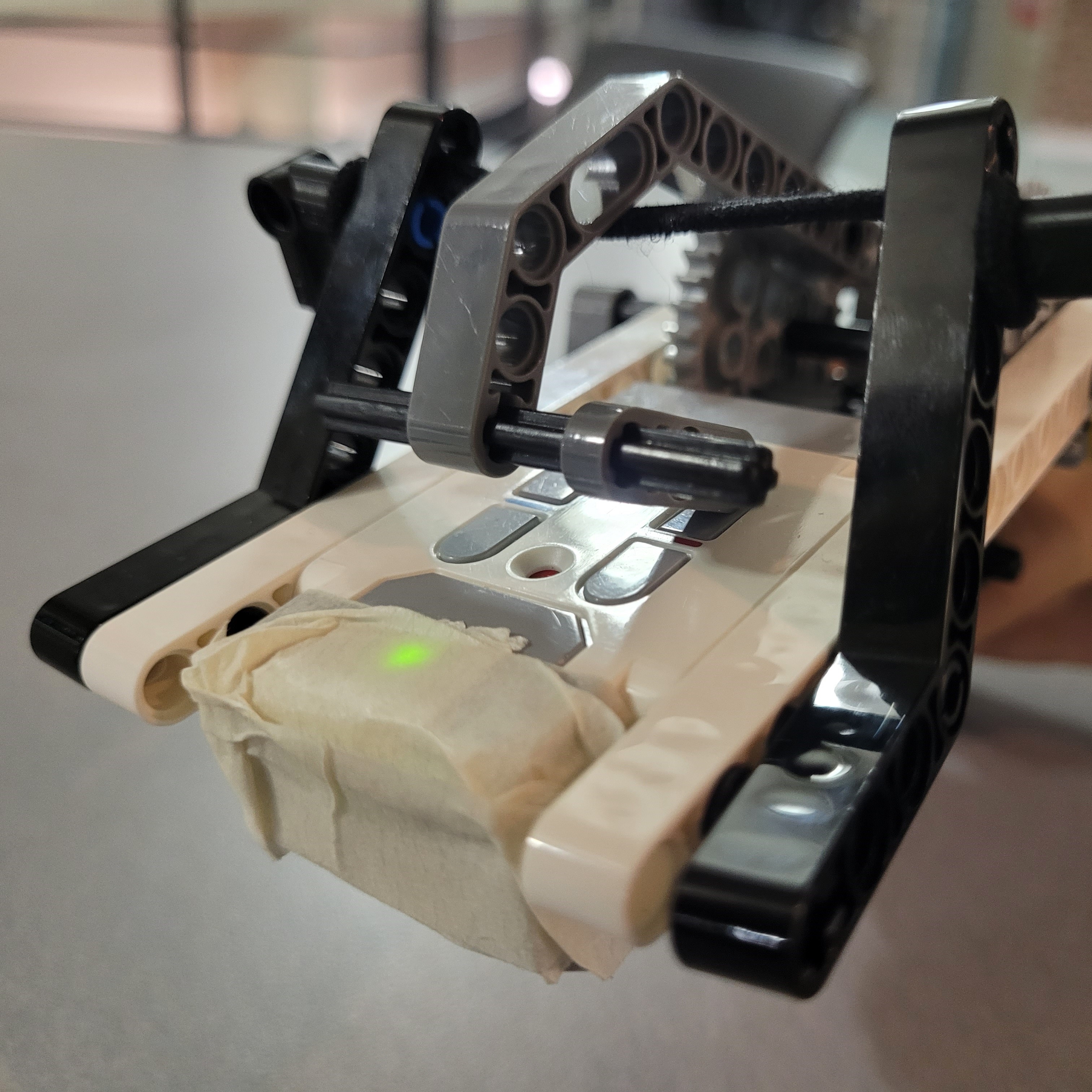
What?
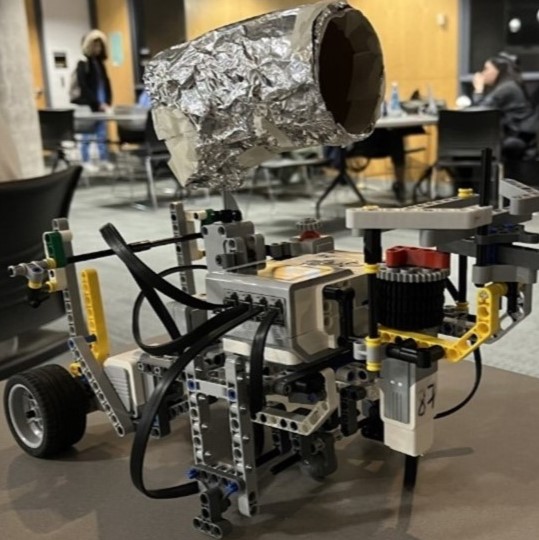
An interactive miniature desktop laser-tag robot! Made from a Lego EV3 brick, Lego components, and RobotC. As a final project for MTE100 and MTE 121 courses, the laser tag robot was a
group effort with fellow Mechatronics students: Akshaya Thavakumar, David Yen, and Nithila Rajaratnam.
Game Play
A game of laser-tag is initiated when the player chooses between the specified game intervals on the robot interface.
The robot then begins gameplay and navigates the desktop surface randomly while avoiding falling off table edges.
The player uses the wireless gun to take shots at the robot. If the user shoots at the robot accurately,
the robot will count a point and display the final score at the end of the game. If a player chooses to terminate the game
before the specified game time ends, a killswitch located on the robot will end all programs when triggered.
How Does it Work?
The laser-tag system was comprised of 2 components, the robot body and the gun. The robot used 3 total motors (1 large, 2 medium) and had 4 unique types of inputs: an infared sensor, motor encoders, touch sensor, and an ultrasonic sensor.
Skills Applied